使用注解配置spring
1.导入约束
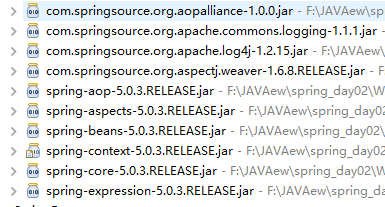
2.导包 新版的spring再使用注解时需要导入spring-aop
3.启用注解 base-package 指定扫描哪个包下的类文件,会扫描指定包下的子孙包
<context:component-scan base-package="leitao.zhang.entities"></context:component-scan>
spring bean常用注解
1.@Component: 组件 作用在类上 ,其有三个相同的注解
* @Controller :WEB 层
* @Service : 业务层
* @Repository : 持久层
这三个注解是为了让标注类本身的用途清晰,Spring
2.属性注入的注解:( 使用注解注入的方式, 可以不用提供 set 方法.)
@Value :用于注入普通类型.
@Autowired :自动装配: 如果有相同类型的多个对象其实会出现未知问题 比如在注解或配置文件中都有配置
* 默认按类型进行装配.
* 按名称注入:
* @Qualifier:强制使用名称注入.
@Resource 相当于:
* @Autowired 和@Qualifier 一起使用
注意:这些注解也可以用于set方法,两者效果是一样的 区别在于:在属性上面加注解是利用反射来完成赋值的,而在set方法上是通过set方法赋值的
3.Bean 的作用范围的注解
@Scope:
* singleton: 单例
* prototype:多例
4.Bean 的生命周期的配置
@PostConstruct :相当于 init-method
@PreDestroy :相当于 destroy-method
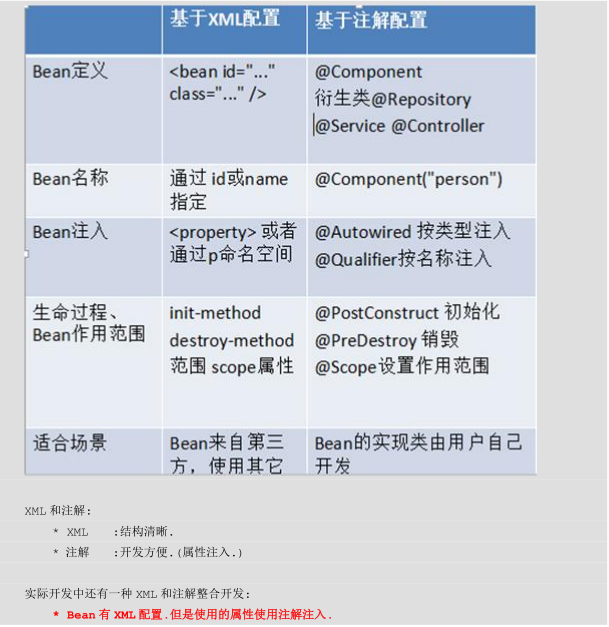
5.Spring 的 的 Bean 管理的方式的比较
package leitao.zhang.entities;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("user")
@Scope("singleton")
//@Controller("user")
//@Service("user")
//@Repository("user")
public class User {
public User() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
@Value("张三")
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Car car;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
@Value("36")
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Car getCar() {
return car;
}
@Autowired
@Qualifier("car")
@Resource(name="car")
public void setCar(Car car) {
this.car = car;
}
@PostConstruct
public void init()
{
}
@PreDestroy
public void destory()
{
}
}
Spring AOP
什么是AOP?
在软件业,AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
Spring中AOP实现的两种方式
* JDK 的动态代理 :针对实现了接口的类产生代理.
* Cglib 的动态代理 :针对没有实现接口的类产生代理. 应用的是底层的字节码增强的技术 生成当前类
的子类对象.
jdk动态代理实例
接口:
package leitao.zhang.entities;
public interface People {
public void say(String name);
}
实现类:
package leitao.zhang.entities;
public class ZhangBaiZhi implements People {
public void say(String name) {
System.out.println(name+",您好,我是张柏芝~");
}
}
自定义动态代理:
package leitao.zhang.proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class ProxyFactory<T> implements InvocationHandler{
private T obj;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T getProxy(T obj)
{
this.obj = obj;
T object = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ProxyFactory.class.getClassLoader(),obj.getClass().getInterfaces(),this);
return object;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("方法"+method.getName()+"调用前,do someting");
Object invoke = method.invoke(this.obj, args);
System.out.println("方法"+method.getName()+"调用后,do someting");
return invoke;
}
}
测试动态代理:
package leitao.zhang.proxy;
import leitao.zhang.entities.People;
import leitao.zhang.entities.ZhangBaiZhi;
public class ProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ZhangBaiZhi zhangBaiZhi = new ZhangBaiZhi();
ProxyFactory<People> factory = new ProxyFactory<People>();
People proxy = factory.getProxy(zhangBaiZhi);
proxy.say("张三");
}
}
输出结果:
方法say调用前,do someting 张三,您好,我是张柏芝~ 方法say调用后,do someting
导包
4(核心包)+2(日志包)+2( AOP 的开发的包:spring-aop,com.springsource.org.aopalliance)+2(aspectj 的开发包:spring-aspects)
导入约束
名词解释
- Joinpoint(连接点):所谓连接点是指那些被拦截到的点(可增强的方法)。在 spring 中,这些点指的是方法,因为 spring 只
支持方法类型的连接点. - Pointcut(切入点):所谓切入点是指我们要对哪些 Joinpoint 进行拦截的定义.(已增强,或要增强的方法)
- Advice(通知/增强):所谓通知是指拦截到 Joinpoint 之后所要做的事情就是通知.通知分为前置通知,后置
通知,异常通知,最终通知,环绕通知(切面要完成的功能) - Target(目标对象):代理的目标对象
- Weaving(织入):是指把增强应用到目标对象来创建新的代理对象的过程.spring 采用动态代理织入,而 AspectJ 采用编译期织入和类装在期织入
- Proxy(代理):一个类被 AOP 织入增强后,就产生一个结果代理类
- Aspect(切面): 是切入点和通知(引介)的结合
- Introduction(引介):引介是一种特殊的通知在不修改类代码的前提下, Introduction 可以在运行期为类
动态地添加一些方法或 Field.
准备(切面类)通知类
package leitao.zhang.spring.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
//通知类
public class MyAdvice {
//前置通知
// |-目标方法运行之前通知
//后置通知(如果出现异常不会调用)
// |-在目标运行之后调用
//环绕通知
// |-在目标方法前后调用
//异常拦截通知
// |-如果出现异常,就会调用
//后置通知(无论是否出现异常都会通知)
// |-在目标方法运行之后通知
//前置通知
public void before()
{
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
//后置通知
public void afterReturning()
{
System.out.println("后置通知,出现异常不会被调用");
}
//环绕通知
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable
{
System.out.println("环绕前置通知");
Object proceed = pjp.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕后置通知");
return proceed;
}
//异常通知
public void afterException()
{
System.out.println("异常时调用");
}
//后置通知
public void after()
{
System.out.println("后置通知,总会被调用");
}
}
xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd "> <bean name="userDao" class="leitao.zhang.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean> <bean name="myAdvice" class="leitao.zhang.spring.aop.MyAdvice"></bean> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(public * leitao.zhang.dao.impl.*DaoImpl.*(..))" id="pc" /> <aop:aspect ref="myAdvice"> <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pc" /> <aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="pc" /> <aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut-ref="pc" /> <aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pc" /> <aop:after-throwing method="afterException" pointcut-ref="pc" /> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>
切入点表达式
execution(表达式)
表达式:
[方法访问修饰符] 方法返回值 包名.类名.方法名(方法的参数)
- public void leitao.zhang.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl.add(args) 完整表达式
- public * leitao.zhang.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl.add(..) 任意返回值和任意参数
- * leitao.zhang.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl.add(..) 省略访问修饰符
- * leitao.zhang.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl.*(..) 指定包下所有的方法
- * leitao.zhang.dao.impl.*DaoImpl.*(..) 包后缀是DaoImpl下所有方法
- * leitao.zhang.dao.impl..*.*(..) 包impl下所有子孙包所有方法
测试 凡是匹配到表达式的bean 获得都是增强后的对象
package leitao.zhang.spring.aop;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import leitao.zhang.dao.UserDao;
public class TestSpringAop {
@Test
public void func1()
{
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("leitao/zhang/spring/aop/applicationContext.xml");
UserDao bean = (UserDao) ac.getBean("userDao");
bean.add();
}
}
AOP注解配置(了解内容)
配置xml bean 也可以用注解
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy /> <bean name="userService" class="leitao.zhang.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"></bean> <bean name="myAnanotionAdvice" class="leitao.zhang.spring.aop.MyAnanotionAdvice"></bean>
通过注解配置
package leitao.zhang.spring.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
@Aspect
public class MyAnanotionAdvice {
//声明一个切入点 方法仅仅是为了标志
@Pointcut("execution(* leitao.zhang.service.impl.*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void pc()
{
}
@After("MyAnanotionAdvice.pc()")
public void after()
{
System.out.println("后置操作,出现异常一会调用");
}
@Before("execution(* leitao.zhang.service.impl.*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before()
{
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(* leitao.zhang.service.impl.*ServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void afterReturning()
{
System.out.println("后置通知,出现异常不会被调用");
}
}
学习过程中 发现的这篇博文,具有参考补充的作用
http://blog.csdn.net/autfish/article/details/51184405
https://www.cnblogs.com/leehongee/archive/2012/10/01/2709541.html
未经允许不得转载:开心乐窝-乐在其中 » 注解配置spring和spring中的aop